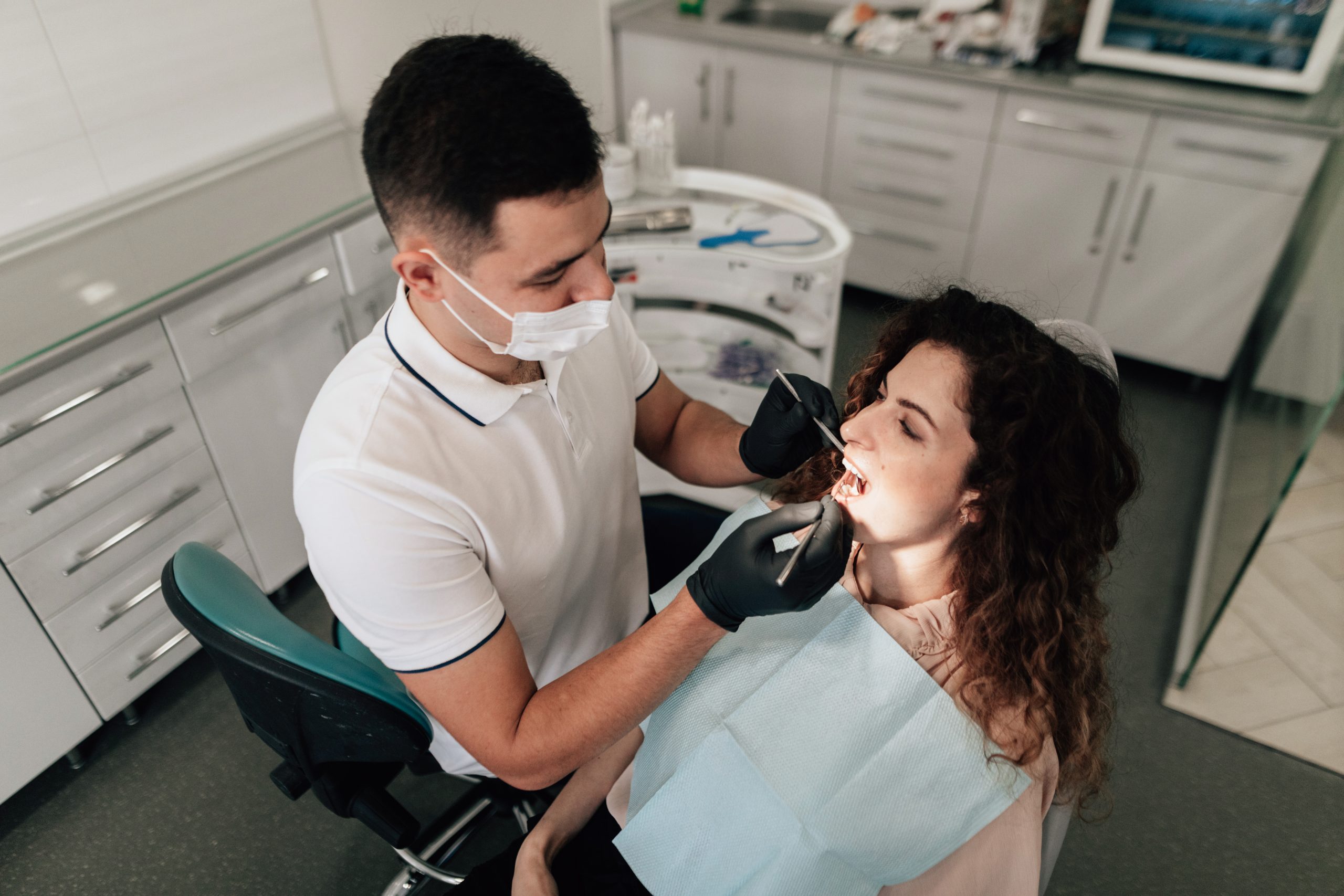
Common Oral Infections And Their Symptoms
Oral infections can affect us in the early years or in adulthood. If left untreated, these infections can leach into the bloodstream and affect other organs, causing a myriad of health problems. A weaker immune system can also exacerbate the extent of the infection in your mouth, which is why oral diseases are most common in children and older adults.
6 Most Common Oral Infections
1. Dental Cavities
Dental cavities or dental caries, happen when there is enamel damage and results in small holes in the tooth. The bacteria in the mouth feed on the sugar from the food you eat and convert these sugars into acids. Gradually, plaque is formed and results in further enamel decalcification and subsequent tooth decay.
A diet high in sugar and the bacteria in your mouth that feed on that sugar, called Streptococcus mutans, are responsible for tooth decay and are a leading cause of tooth loss in children. If left untreated, the tooth will decay further and more extensive treatment will be required.
2. Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease and is caused by different strains of bacteria in the mouth. Bacteria that settle in the gum line release toxins and trigger an inflammatory immune response. The gums swell and can bleed on impact, e.g. when brushing your teeth.
This condition can be managed with regular brushing and flossing to remove the bacteria in the gum line and also with dental treatments. Gingivitis can worsen into periodontal disease without early intervention.
3. Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease is gingivitis that has spread below the gum line and affects the bone and supporting tissue. The gums start to recede and pockets of pus from around and underneath the teeth, inevitably result in inflammation and bone loss. Gradually the teeth become unstable and tooth loss occurs. Gum disease is the number one cause of tooth loss in adults.
4. Canker Sores
Canker sores, otherwise known as aphthous ulcers, are lesions that form on your gum line or other soft mouth tissues. The causes are uncertain but are thought to be things like stress, hormone changes, weakened immunity, and food sensitivities.

They appear as small white sores and usually disappear on their own after 10-14 days.
5. Oral Herpes
The herpes simplex virus, or HSV-1, is the cause of oral herpes infection and around 70% of adults in the UK are carriers of the virus. Exposure to the virus can involve flu-like symptoms, fluid-filled blisters, and ulcers in and around the mouth. There also may be no symptoms at all, which is what makes it so hard to detect.
Once infected, the virus stays in the body permanently and is also contagious, so avoid touching your sores and steer clear of oral contact with anyone. Outbreaks can occur more than once and can last from a week to 10 days.
Children can sometimes develop herpes gingivostomatitis – this is where the gums swell and blisters form. These heal by themselves, and the virus stays dormant for the most part, but it can flare up in instances like stress or trauma.
6. Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is caused by the virus ‘Coxsackie A16’ and usually affects children under the age of 12. The symptoms consist of a sore throat and fever and painful blisters on the tongue and cheeks, palms, soles of the feet, and buttocks. The symptoms usually subside after three days.
Herpangia is a condition related to hand, foot, and mouth disease that showcases similar symptoms. The blisters form at the back of the mouth and on rupturing, they can cause large ulcers to form. It typically lasts 3-5 days.
By practising basic oral hygiene, like brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and limiting bad habits like smoking and drinking too much coffee, we can prevent diseases like tooth decay.